First, if you had tried to use the Device Manager remotely you would have received a nice "Access is denied" error message. This can be resolved by editing a local policy: Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\System\Device Installation\Allow remote access to the Plug and Play interface. [You have to reboot for the policy to take effect.]
Instructions for this can be found here. But unlike what the article indicates, you do not get the ability to edit devices. Maybe that works in Server 2008, but in Server 2008 R2 you only get read-only access.
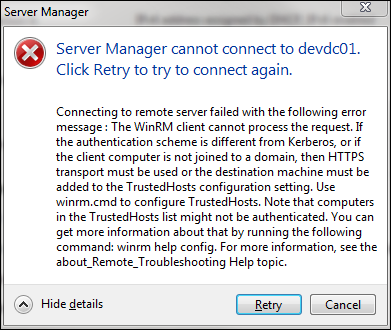
Second, and probably more important, when you try to connect to your Server Core via Server Manager from another machine in the workgroup, you will receive the following error:
The solution to the problem is found in this TechNet article. You can follow the instructions in the Note section which says to run the following command on the source computer. (By "source computer" they mean the computer that you’re using to connect to Server Core.)
winrm set winrm/config/client @{TrustedHosts="ServerCoreMachineName"}
I’m sure that works fine, but I did something different. I read somewhere else about that fact that this setting exists in local policy. Run gpedit.msc, and navigate to Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\Windows Components\Windows Remote Management\WinRM Client\Trusted Hosts. You can enter multiple hosts using this method, or in my case just allow all hosts.
And just like that, Server Manager works over a workgroup.

Do you manage IIS from a workgroup as well?
ReplyDeleteYes, it can be done. Your server running IIS needs to be running the management service for IIS and it needs to be enabled. If your box is running server core, you can do this with PowerShell, Enabling IIS Remote Management – Remotely using PowerShell. If your box is running normal Windows GUI you can install this service from Server Manager, then enable remote management from the IIS Management console. Once that is done, you can remotely manage IIS from your workgroup machines. Once more caveat - if you're trying to do the remote management from a workstation (Win 7), then you need to install IIS Manager for Remote Administration. The IIS Management Console that comes with Windows 7 cannot manage remote servers. Hope that answers your question.
DeleteI forgot to mention I wanted to manage a server (2008 R2 Core) not on my domain (In DMZ allowing WinRM ports), from a Win 7 PC on my domain. I have done what you have said above, but it still fails to authenticate. I could probably use IIS Manager users, but in order to access IIS to add the users I had to add the server back into my domain so I could authenticate to IIS, make the changes and remove from domain again. I could have probably used the powershell to do this, but I was running short of time to check it out. I haven't found anything on accessing it in this way.
DeleteIIS Remote Management uses port 8172 - is that open between your Windows 7 domain PC and your R2 Core DMZ server? Depending on how you setup IIS remote management on your core server, perhaps the firewall rule didn't get created? I haven't tried this myself. Or maybe there is an additional firewall between your domain and the DMZ? When this is done in the Windows GUI, a firewall rule is automatically created called Web Management Service (HTTP Traffic-In).
Delete